In the quest for space exploration, the propulsion systems that power the spacecraft determine the success of a mission. Direct fusion drive (DFD) is one of the latest technologies that has the potential to revolutionize the space industry. This state-of-the-art technology can simplify the space exploration journey while saving time and operational costs.

Image Credits: Wikimedia Commons
What is the Direct Fusion Drive?
Unlike traditional power systems that rely on combusting propellants, direct fusion drive is a nuclear fusion-based engine that produces thrust and electricity to power the spacecraft. The system generates power through nuclear fusion using a heating and magnetic confinement fueled with deuterium (hydrogen isotope) and helium. This advanced technology enhances efficiency and rocket speed, thereby- completing the missions on time without adding extra fuel costs.
How Does the Direct Fusion Drive Technology Work?
The system uses a fusion engine that produces plasma, a collection of charged particles that release enormous amounts of energy. The plasma undergoes nuclear fusion in the controlled magnetic fields to produce energy which is converted into thrust, powering the spacecraft. The application of fusion in direct fusion drive makes it a sustainable alternative to traditional propelling systems.
Advantages And Challenges With Direct Fusion Drive
According to the Princeton Satellite System, an aerospace research and development firm, the DFD technology may produce 1 to 10 Newtons of thrust per fusion power. Approximately, 35 percent of the energy converts to thrust, 30 percent to electric power, 25 percent is lost as heat, and the remaining 10 percent is changed into radio-frequency heating. This technology could power a spacecraft for deep space missions. Further, a direct fusion drive for interstellar exploration facilitates longer missions while eliminating the need for extra fuel. Besides, the technology also seems an environmentally friendly option as it produces less waste and relies on hydrogen isotopes to promote clean energy.
Furthermore, scientists are working on improving efficiency, overcoming technology problems, and increasing the technology’s reliability to deal with challenges.
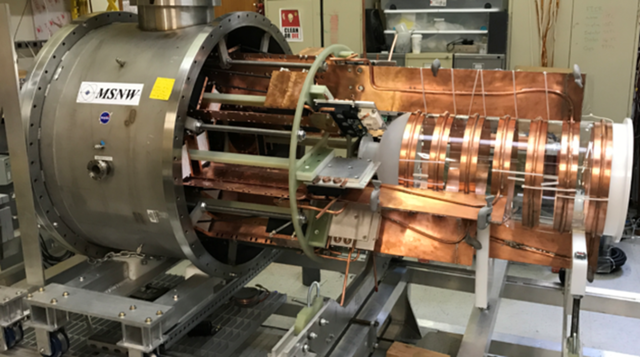
Image Credits: Wikimedia Commons
Future Projects
NASA is building a nuclear-powered, direct fusion drive-based lander for Titan, one of Saturn’s moons, as a part of the Dragonfly mission. It will launch in 2027, and this will be the first mission to land a rotorcraft on the planet’s moon. Also, this direct fusion drive 2027 will be the first-ever scientific payload to run on nuclear power.
The Impact of Direct Fusion Drive on Humanity
Space exploration and humanity are linked. Latest space technologies like direct fusion drive could open opportunities for exploration and colonization. Further, it could fasten the space programs while ensuring safety and saving fuel and costs for comfortable travelling. Unlike conventional missions, it can be a sustainable option that contributes to environment-friendly space missions. Also, the technology can open the door to multiple economic opportunities, from research to manufacturing and managing operations. This can create jobs in the space industry that give a boost to economic growth.
If you enjoyed reading our articles, please support us by buying our geeky merchandise on Instagram. Alternatively, you could buy us a coffee or follow us on Facebook, Twitter, Pinterest, or Medium.



1 comment
[…] to propel the spacecraft at unprecedented speeds, placing them in their intended orbits for deep-space explorations. Both methods offer unique advantages, enabling spacecraft to travel faster and more […]